 Skin discoloration is a common skin problem, and this can come in the form of white spots, dark spots or other changes in skin color. White spots on skin usually indicate a loss of skin pigmentation, and these may occur as small spots or large patches that may appear anywhere in the body, including the neck, shoulders, upper back, the shins, and the forearms. They do not usually cause pain, itching, or irritation, but they usually cause distress, especially in people with darker skin, where the contrast in skin color is more obvious.
Skin discoloration is a common skin problem, and this can come in the form of white spots, dark spots or other changes in skin color. White spots on skin usually indicate a loss of skin pigmentation, and these may occur as small spots or large patches that may appear anywhere in the body, including the neck, shoulders, upper back, the shins, and the forearms. They do not usually cause pain, itching, or irritation, but they usually cause distress, especially in people with darker skin, where the contrast in skin color is more obvious.
White spots may occur in people of all races or skin color. They affect both sexes, and are common in people who live in hot, humid climates. Some white spots develop into brown spots covered by whitish scaly skin. This type of white spots may be accompanied by itching.
Causes of White Spots on Skin
There are many possible causes of white spots, but the most common is vitiligo.
1. Vitiligo
White patches that develop on many areas of one's skin are usually caused by vitiligo.
Causes: Vitiligo is a condition characterized by the loss of skin pigment called melanin, which is normally produced by cells called melanocytes. Discoloration is caused by the destruction of the melanocytes, but the exact cause is not known. One mechanism that has been proposed involves the body's immune system, which destroys its own cells, which is characteristic of autoimmune disease.
Risk Factors: Around 2-5 million Americans or up to two percent of the US population are affected by vitiligo. The white spots usually appear early, between the first and third decades of life. Men and women are equally affected. Risk factors include:
- Family history of vitiligo
- Premature graying of hair
- Autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Symptoms: A rapid loss of skin pigmentation often indicates the development of vitiligo. However, it may also be followed by a period of stability where the condition does not seem to progress. Cycles of rapid whitish discoloration and stability may follow.
White spots on skin due to vitiligo usually affects the exposed body parts and skin folds (like the armpit), but may also affect areas of previous injury, skin around moles or body openings. It can also be observed on the hair and eyelids.
Once the white spots have developed, the skin may not return to its normal color.
Diagnosis and Treatment: The diagnosis of this skin condition is easily made by a doctor after taking a medical history and physical examination. However, one can neither prevent nor permanently cure vitiligo. The goal of treatment is to improve the physical appearance of the skin using cosmetics to camouflage the white spots, inducing re-pigmentation using corticosteroid treatment or phototherapy, reducing the pigmentation of unaffected area, and by skin grafting.
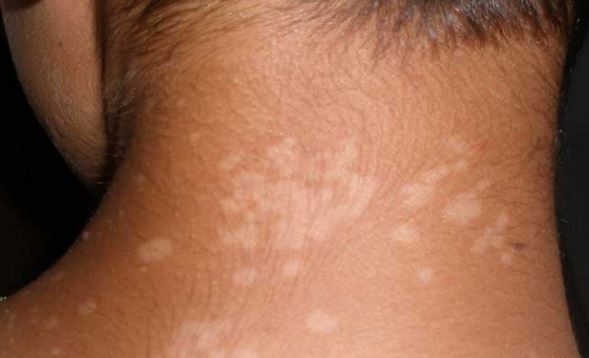
2. Tinea Versicolor
Tinea versicolor or ptyriasis versicolor is another common and harmless skin condition that affects skin color.
Causes: It is caused by yeast called Malassezia, which normally exist in small numbers on the skin. Certain conditions however, can cause the overgrowth of the yeast, causing the development of white and reddish-brown spots on skin. Moist, warm, and oily skin encourages yeast overgrowth especially in the upper arms, neck, abdomen, and thighs. It is not a contagious disease.
Risk Factors: Conditions that lead to the appearance of white spots on the skin related to tinea versicolor include warm and humid climate, excessive sweating, oily skin, malnutrition, pregnancy, medications such as corticosteroids, or any factor that may weaken the immune system.
Treatments: Antifungal medications such as terbinafine, clotrimazole, or miconazole may be used to treat the infection. Shampoo containing selenium sulfide may be applied as a lotion on affected skin before bedtime. This may be rinsed off in the morning. One should consult a dermatologist if symptoms persist after these over-the-counter treatments applied for at least two weeks.
3. Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis
White spots that are flat and measure about two to five millimeters in diameter are characteristic of a skin condition known asidiopathic guttate hypomelanosis. Although they are often smooth, they can also become scaly. They are common among women and in people with fair skin, but they may also occur in people with darker skin tones. They are usually seen on areas of the body exposed to the sun such as the face, forearms, shoulders, and shins.
Causes: Its name (idiopathic) indicates that the cause is unknown. However, the appearance of the white spots on skin seems to be associated with natural aging, since they occur in individuals older than 40 years. Hereditary factors may be involved because this skin problem seems to run in families.
Risk Factors: Women, fair skin, hereditary factors and aging are among the risk factors leading to the development of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis.
4. Pityriasis Alba
This common skin discoloration affects children and adolescents. This condition is characterized by the appearance of dry, scaly white patches on one's face. These white skin patches are more visible during summer because of tanning in the surrounding skin. In winter, patches become dry and scaly. Raised reddish spots may appear and later turn pale, becoming smooth and flat patches. They are often found on the neck, shoulders, upper arms, and face. The cause is unknown.
5. Malnutrition
White spots on skin may also be due to malnutrition. Deficiencies in calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin E can lead to the appearance of white patches on the skin. These skin marks are harmless but they indicate that you need to eat a healthy balanced diet to prevent discoloration of the skin. Consult a doctor for advice regarding taking dietary supplements for healthy skin.
6. Nevus Depigmentosus
This type of skin depigmentation is easily differentiated from vitiligo because the white spots are permanent or stable in nature. The skin is not totally achromatic and hair found on the skin area is often white.
7. Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation is defines as loss of color in the skin. This occurs when the melanocytes (pigment-producing cells in the skin) are depleted or when the amino acid called tyrosine decreases. This reduces of the production of skin pigments called melanin. Thus, white spots on skin are due to depletion of melanin in the skin.
