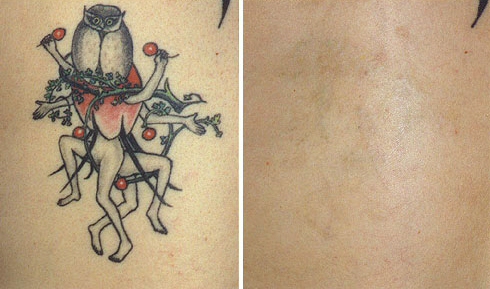
With the advancement in medical science, now it has become possible to even remove the "permanent" skin tattoos. A significant percentage of people with body tattoo regretting getting the tattoo. Earlier, not many effective methods with good success rate were available. However, now various techniques have been developed that are less painful and provide excellent results.
Laser Tattoo Removal
Currently using laser to remove tattoo is considered the best method. The three most commonly used laser types are Q-switched Nd: YAG laser, Q-switched Alexandrite laser and the Q-switched Ruby laser.
Tattoos are basically a pigment injected into the dermal layer of the skin. The laser light when applied to tattoo causes the breakdown of this injected pigment. The phagocytes (a cell part of the immune system) in the skin slowly remove these small fragments of tattoo pigments over a course of several weeks. Often, the treatment is needed in more than one session to completely remove the pigments. This procedure causes burning pain and often a local anesthetic like lignocaine is applied before the procedure. Post-treatment, topical antibiotics are not needed. Moreover, they can cause allergic reaction.
A related technique is intense pulsed light therapy (IPL) in which high intensity light is used instead of lasers. This technique is more expensive than laser therapy and its relative advantages over the laser therapy are still a matter of debate.
Dermabrasion
Here is another tattoo removal method. Dermabrasion involves freezing the tattoo area by spraying a freezing solution. The skin is then gently peeled off with an abrading device. This procedure is painful and causes bleeding after the abrasion. Dressing is needed after the procedure because of the bleeding. A similar procedure is salabrasion in which saline solution is used instead of freezing solution and then the tattoo area is abraded using an abrading device. These procedures are painful and usually a local anesthetic is pre-applied before the procedure.
Excision
The tattoo area is surgically excised and resultant wound closed. For larger tattoos, a skin flap from some other part of the body might be needed after the excision. The surgery is done under local anesthesia. A related technique is cryosurgery, in which area is frozen first, and then excised.
Results and Complications
After a procedure, some skin color changes usually persist. Complete tattoo removal and restoration of absolutely normal skin color and texture is often not possible. However, the results are very promising. The final results depend upon a number of factors, the most important ones are:
- Person's ability for wound healing: Impaired wound healing may result in scarring or altered pigmentation of the skin.
- Age of tattoo: New tattoos are more difficult to removal.
- Expertise of the artist: Tattoos by experienced tattoo artist are easier to remove because of proper injection of the dye in the correct layer of the skin.
- The type of tattoo ink used: Nearly 100 different types of inks are being used. Some are easier to remove compared to others. Blue and black colored inks are easiest to remove.
- Size and location of the tattoo.
After procedure, there may be some scarring of the treated area. Scarring specially occurs with abrasion techniques and excision. The wound may become infected if proper care is not taken.
Laser removal might be associated with increased or decreased pigmentation in the treated area (hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation). Scarring can also occur after laser removal. Some tattoo may persist despite repeated sessions of laser treatment. Local allergic reaction to breakdown products of the tattoo pigment may occur. Rarely, darkening of the tattoo may occur after laser therapy.